2015, Volume 22, Issue 4, pages 121–160

2015, Volume 22, Issue 4, pages 121–160
Editorials Clinical articles News and viewsTopics include:-
- Lipids in high-risk CVD: a large UK study
- CoQ10 and cardiovascular disease
- Atypical chest pain in young adults
Editorials
Back to top
December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:134–5 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.039
Impact of latest NICE guidelines on CRT and ICD implant rates
Andrew J Turley

Cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) have an unquestionable evidence base in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), already on optimal medical therapy. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) effectively treat ventricular arrhythmias, which account for up to 50% of mortality in patients with reduced LVEF.1 Likewise in appropriately selected patients, cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT) reduces hospitalisation rates, improves symptoms and prolongs life-expectancy.2

December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:132–3 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.038
Surgeon-specific mortality data are misleading and harmful
Ravi De Silva

The Government is soon to publicly disclose a league table for cardiac surgical units within National Health Service (NHS) England. While this information may be useful and raise questions as to why one unit may be better or worse than another, we are also to be made aware of surgeons who are performing significantly better or worse than expected in terms of risk-adjusted mortality. But are patient deaths following surgery caused exclusively by the surgeon, as surgeon-specific mortality data (SSMD) would imply? And is the surgeon with the lowest operative mortality the best doctor? In my opinion the answer to both these questions is a resounding no.

October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:130–1 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.032
‘The age of no retirement’: implications for the health of the nation
Jonathan Collie

Life-expectancy is now approaching 90 years, and it won’t stop there. Healthy life-expectancy is also extending, so that the average 60 year old can expect a further 11 years of healthy life. Currently, 35% of the UK population is over 50 years, and growing – and on the whole they are healthier, more skilled, better educated and more dynamic than ever before.

October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:127–9 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.033
Statins and myalgia: fact or fiction?
Peter Sever

Contemporary guidelines have lowered the threshold for statin use in primary prevention (7.5% risk of a cardiovascular event over 10 years in the USA,1 10% risk according to National Institute for Health and Care Excellence [NICE] guidelines in the UK).2 Applying these thresholds, the majority of men over 50 years and more than half of women over 60 years will qualify for statin use. Countering the more widespread uptake of statin use in primary prevention advocated by these guidelines are claims, popularised by the lay press and uncritically published in some medical journals,3,4 that statin use is accompanied by an unacceptable incidence of side effects that adversely compromise lifestyle and which challenge whether the small absolute benefits in some lower risk groups are worth the intolerance of the statin.
Clinical articles
Back to top
December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:155 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.041
Latest NICE guidelines on CRT and ICD devices in heart failure may significantly increase implant rates
Thabo Mahendiran, Oliver E Gosling, Judith Newton, Dawn Giblett, Dan McKenzie, Mark Dayer

In June 2014 the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) released new guidelines (TA314) on the use of implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) and cardiac resynchronisation therapy devices (CRTs) in the management of heart failure. These guidelines replaced the previous TA95 and TA120 guidelines. We evaluated the potential impact on implant rates in our institution.
Clinical records of 396 consecutive patients were reviewed, with 100 patients included in the final analysis. Device indications and associated costs were calculated using both existing and new criteria.
NICE TA95/TA120 criteria recommended 37 devices: 20 ICDs, 9 CRTs with pacing (CRT-Ps), and 8 CRTs with defibrillator (CRT-Ds). The new NICE 2014 criteria recommended 97 devices: 56 ICDs, 7 CRT-Ps, and 34 CRT-Ds. Comparison of the new and old guidelines suggested a significant increase in total devices (p<0.0001). This corresponded primarily to an increase in ICDs and CRT-Ds, with an associated £661,708 increase in total spend (£407,205 increase per annum).
This study confirms the significant increase in ICDs and CRT-Ds indicated by NICE. This will have significant financial and workforce implications.

December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:136 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.040
Barriers to cardiac device innovation
Nick Linker

The UK population is getting older and the amount of cardiovascular disease is increasing significantly, fuelled by a steep rise in the incidence of obesity and diabetes. Heart failure is increasing in incidence because of improved survival rates following myocardial infarction and more effective treatments, with an estimated 500,000 sufferers.1 People with heart failure are more at risk of sudden cardiac death and many can benefit from cardiac devices such as implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) and cardiac resynchronisation devices (CRT-D/Ps). This increasing need was recognised by the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in 2014 with the publication of the revised guidelines for the use of such devices.2 Nevertheless, the UK remains well below the European average for ICD implants, although is improving in terms of CRT devices;3 the latter due to a higher than average implant rate of CRT pacemakers. However, the rate of implantation of all high-energy devices (ICD + CRT-D) is only slightly more than half the European average.
December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:156 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.042
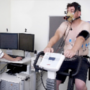
Healthcare professional’s guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing
Sathish Parasuraman, Konstantin Schwarz, Nicholas D Gollop, Brodie L Loudon, Michael P Frenneaux

Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPEX) is a valuable clinical tool that has proven indications within the fields of cardiovascular, respiratory and pre-operative medical care. Validated uses include investigation of the underlying mechanism in patients with breathlessness, monitoring functional status in patients with known cardiovascular disease and pre-operative functional state assessment. An understanding of the underlying physiology of exercise, and the perturbations associated with pathological states, is essential for healthcare professionals to provide optimal patient care. Healthcare professionals may find performing CPEX to be daunting, yet this is often due to a lack of local expertise and guidance with testing. We outline the indications for CPEX within the clinical setting, present a typical protocol that is easy to implement, explain the key underlying physiological changes assessed by CPEX, and review the evidence behind its use in routine clinical practice. There is mounting evidence for the use of CPEX clinically, and an ever-growing utilisation of the test within research fields; a sound knowledge of CPEX is essential for healthcare professionals involved in routine patient care.

December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:158 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.043
A region-wide audit of cardiac rehabilitation services
M Justin S Zaman on behalf of all ACRAN healthcare professionals

This is an audit of 10 Anglia region cardiac rehabilitation (CR) programmes against the British Association of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation (BACPR) seven core standards. Methods included a questionnaire that encapsulated these standards, a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis and assessment of local outcomes.
Overall, all 10 CR services were compliant with the vast majority of basic standards set by BACPR but the audit also highlighted gaps in ideal care processes, such as a shortage of psychologists, occupational therapists and pharmacists, and inadequate audit processes. Local strengths were highlighted that will encourage future cross-pollination across the network. Outcomes were collected variably ad hoc but there was some consistency that CR across the region improved exercise tolerance, reduced anxiety and reduced smoking, but had little effect on blood pressure and body mass index, comparable to the national audit.
Anglia CR services were shown to be fit-for-purpose and there were local areas of excellence, but local areas of need and gaps in CR were highlighted that will cross-pollinate to improve all CR services in East Anglia.

October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:147–54 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.034
Treatment patterns and lipid levels among patients with high-risk atherosclerotic CVD in the UK
Beth L Nordstrom, Jenna M Collins, Robert Donaldson, William A Engelman, Antje Tockhorn, Yajun Zhu, Zhenxiang Zhao

High-risk atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), including recent history of acute coronary syndrome, cerebrovascular atherosclerotic disease, peripheral arterial disease, and coronary artery disease with diabetes mellitus, requires lipid-level monitoring and treatment. Data for patients with high-risk ASCVD from 2008–2011 were obtained from the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Across two years of follow-up, analyses examined lipid-altering drug use, statin adherence (medication possession ratio [MPR]), and persistence (continuous time on drug). Initial statin dose, upward dose titration, and use of high-intensity statins were also studied. Lipid levels were examined overall and by statin use. A total of 131,603 high-risk ASCVD patients were included. Within six months of diagnosis, 63.1% of patients received a statin prescription. Patients typically remained on the initial statin (MPR ≥80% for 71.3% of patients at two years) and dose; 16.4% of patients used high-intensity statins. During the first year of follow-up, 69.3% of patients were either at the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal of <2.5 mmol/L or using a high-intensity statin. Considerable room for improvement remains with respect to optimal management of patients with ASCVD.

October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:157 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.035
Pre-alert calls for primary PCI: a single-centre experience
Jennifer A Rossington, Stephen F Cole, Yasmin Zaidy, Michael S Cunnington, Richard M Oliver

Hull and East Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust offers a primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) service accessed via a coronary care unit (CCU) nurse-based pre-alert system. We reviewed our pre-alert calls for 2013 to determine their appropriateness and assess whether patients were being correctly accepted/declined for PPCI by comparison with final discharge diagnosis.
There were 1,343 calls received, only 52% had chest pain and electrocardiogram (ECG) changes meeting criteria. There were 508 patients with a discharge diagnosis of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), 89% of whom were accepted directly.
There were 54 cases with a final diagnosis of STEMI initially declined: 14 in cardiac arrest were directed to the emergency department (ED) as per policy; 18 had documented clinical reasons for declining; seven did not meet the criteria. There were 15 patients (3%) with chest pain and ECG criteria declined without a documented reason; three were subsequently accepted after assessment at their local hospital. Patients >80 years, female and with atypical presentation were more likely to be declined.
Of accepted patients, 132 (23%) had a diagnosis other than STEMI at discharge, 65% with an alternative cardiac diagnosis.
In conclusion, patients are frequently referred who do not meet symptom or ECG criteria. Most STEMI patients are appropriately accepted via our pre-alert pathway. Review of pre-alert services is essential to ensure timely and appropriate PPCI.
October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:159 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.036
Atypical chest pain in young adult patients: dropped shoulder syndrome as a cause
Ali Abdul-Latif, Adnan Shakir

Left-sided dropped shoulder syndrome (DSS) can present with anterior chest pain that radiates to the left scapula and arm. Patients with atypical chest pain (ACP) of unknown cause (n=47) were investigated for left-sided DSS. Sixteen patients (34%) were diagnosed with left DSS. All the 47 patients were provided physiotherapy in two groups: the left DSS patients group (n=16) and a control group of 31 patients who did not show the criteria for the diagnosis of DSS.
Fourteen (87.5%) patients reported a satisfactory improvement of the ACP after physiotherapy. Satisfactory improvement has been judged by the reduction of the pain intensity, duration and frequency according to the patient’s report. Two (12.5%) patients showed no satisfactory improvement of the ACP. The control group showed no beneficial effect regarding their ACP after physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy aimed to strengthen the muscles that elevate the shoulder, could provide a treatment for atypical chest pain caused by left-sided DSS.

October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:160 doi:10.5837/bjc.2015.037
Coenzyme Q10 and cardiovascular disease: an overview
David Mantle

Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a naturally occurring vitamin-like substance that has three functions of relevance to cardiovascular function: (i) its key role in the biochemical process supplying cardiac cells with energy; (ii) its role as a cell membrane protecting antioxidant; (iii) its direct effect on genes involved in inflammation and lipid metabolism. Although some CoQ10 is obtained from the diet, most is manufactured within the liver, the capacity for which declines with age. These data therefore provide a rationale for the importance of CoQ10 in cardiovascular function, and its dietary supplementation. The objective of this article is therefore to provide a brief overview of the pharmacology of CoQ10, and its role in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.
News and views
Back to topDecember 2015 Br J Cardiol 2016;23:(1)
Pulmonary hypertension news from AHA and ERS
We report highlights of pulmonary hypertension presentations from the most recently held European Respiratory Society (ERS) congress, held in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, from 26th–30th...
December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:146
Heart Rhythm Congress 2015
The 10th Heart Rhythm Congress was held October 4th–7th 2015 at the International Conference Centre (ICC) in Birmingham. This year’s event hosted a...
December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:145
‘Lipids in the community’ – HEART UK 29th annual conference
‘Lipids in the community’ was the general theme of this year’s HEART UK conference, attended by 200–250 participants, covering primary and secondary care,...December 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:143–4
In brief
News in brief from the world of...October 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:138–142