The NIHR represents the most integrated health research system in the world and is the research arm of the National Health Service (NHS). Its national network enables access to experts and trained staff in all therapeutic specialties across the country and opens up collaboration possibilities between groups with similar research interests.
The NHS: an incredible research resource
- the largest publicly funded health service in the world
- looks after one million people every 36 hours
- all inclusive, free to access, it provides a representative population, with the NHS number a unique identifier for patients so they can be followed through the system
- IT systems introduced into primary care and in regular use since the 1990s mean that records are easily accessible.
- its inclusive nature and the diverse population it serves means that results are often globally relevant.
‘The NIHR is the most integrated health research system in the world’
Opportunities through collaboration
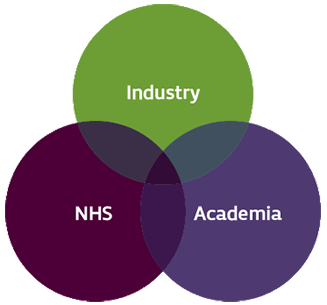
- Addressing new health, scientific and economic challenges involves drawing on strengths from across sectors and requires organisations to collaborate to share expertise, skills and resources within a strong and vibrant innovation ecosystem.
Drawing on different strengths
- Fundamental to this are strong links between academia, industry and the NHS, which act as drivers and adopters of research and innovation.
- The pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical technology industries can adopt more informed approaches to drug, device and diagnostic design and development through collaboration.
- UK academia hosts a strong cohort of investigators with innovative discoveries and ideas arising from detailed explorations of specific diseases. Accurate disease biomarkers developed and validated by academia can improve study protocols, stratify patient populations and ultimately ensure therapy development is more targeted and efficient.
- Partnering with the UK’s world class NHS, including its clinicians, healthcare professionals and dedicated research infrastructure, fosters engagement with patients and their carers. Operating in the context of a unified care system ensures product design is better informed and potentially stratified by patient disease.
Benefits
- Early access to industry compounds and technologies presents academics and clinicians with the opportunity for unique clinical research studies.
- These provide a platform for further research and development, as well as sharing the collective wealth of experience in negotiating the regulatory pathways for research.
The local clinical research networks of the NIHR
Research within the NIHR operates through a single national network – the Clinical Research Network (CRN) – which comprises 15 local clinical research networks and has links with the rest of the UK. It is funded by the Department of Health England and £300 million is invested annually into a research infrastructure comprising over 10,000 specially-trained clinical research professionals who work throughout the NHS and across all disease areas.
The research network has created a thriving environment for conducting large-scale commercial contract clinical research, so that life sciences companies can allocate clinical studies to the UK with confidence. In 2016–17:
- 99% of NHS trusts were actively engaged in clinical research, with 79% delivering commercial contract research studies (up 5% on previous year)
- 48% of General Medical Practices were actively engaged in clinical research (up 6% on previous year).
Trained workforce
International Council for Harmonisation Good Clinical Practice (ICH GCP) training is given free of charge to any staff working on NIHR CRN clinical trials. This provides a research-ready workforce with over 10,000 GCP-trained research staff embedded in the NHS to support investigators with patient identification, recruitment, clinical delivery. The ICH GCP training is supported by the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) and has been added to the list of GCP programs mutually recognised by TransCelerate, an organisation that works to improve the health of people around the world.
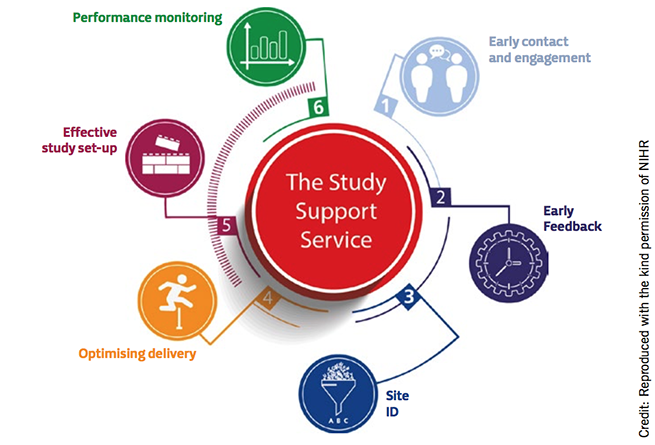
Study support service
To make the greatest impact on study delivery, early engagement with the NIHR can provide access to free support that provides benefits throughout the full lifecycle of the study. A single submission provides you with access to NHS clinical experts across all therapeutic specialties. This can help determine whether the study can be delivered within the NHS, as well as increase the likelihood of delivering the study in a timely manner and meeting recruitment targets.
NIHR can gather expressions of interest from over 240 NHS organisations and over 10,000 general practices in England. This then allows site selection through direct engagement with interested sites. NIHR can provide help with study support costs or on-site research professionals in order to optimise study delivery.
Building on all previous interactions, NIHR can create and implement a study-wide action plan, detailing a single set of recommendations and key information for all study sites that enables a ‘do once and share’ approach. The NIHR data system provides unique access to study-wide recruitment data. When combined with the study-specific review schedule, it enables a proactive approach for identifying and supporting struggling studies.
Furthermore, by having a single point of contact in each region, the NIHR can provide linkages between groups with similar research interests in order to explore the possibility of collaboration.
- More information about this dedicated and integrated NIHR support service can be found at www.supportmystudy.nihr.ac.uk
Some of the NIHR support given during a study
New opportunities for research
There is increasing interest in real-world evidence to support the evidence from randomised controlled trials. The majority of people with long-term conditions are now managed completely within primary care. New models of care within primary care provide an opportunity to develop new models for research.
- Extended hours in primary care facilities can provide better access for researchers and patients.
- Very large practices can provide new models for research beyond the traditional ‘small’ practice model. GP clusters/collaborations of practices (led by GP federations) provide access to large numbers of patients.
- More part-time ‘portfolio’ GPs and other primary healthcare professionals, e.g. pharmacists, physician associates, give dedicated time/staff for research.
- Changes in primary care can facilitate the gathering of these data. It can provide efficient search engines for feasibility and patient identification; and linked IT systems.
- Closer working between primary and secondary care provides hybrid models for research delivery.
Summary
- The NHS is a key driver and adopter of research. The NIHR provides collaboration and networking as well as dedicated and integrated support for clinical research within the NHS.
Articles in the handbook
1. Introduction
3. Optimising clinical research using electronic medical records
4. Recent research at the Institute of Cardiovascular Medicine and Science
5. Clinical trials in the UK from a commercial perspective
6. Brexit: threat or opportunity
7. How to initiate a clinical trial in the UK
8. Useful organisations