Tag Archives: clinical research
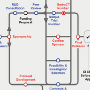
February 2016 Br J Cardiol 2016;23:(1) doi:10.5837/bjc.2016.007 Online First
The barriers facing medical research in the UK
Aaron Koshy, Andrew L Clark
| Full textMay 2009 Br J Cardiol 2009;16:147–150
The prognostic value of raised pre-operative cardiac troponin I in major vascular surgery
Gavin J Bryce, Christopher J Payne, Simon C Gibson, David B Kingsmore, Dominique S Byrne
| Full text

