Tag Archives: vulnerable plaque
February 2011 Br J Cardiol 2011;18:46-9
Contemporary coronary imaging from patient to plaque: part 5 a glimpse of the future
Scott W Murray

Introduction As a way of moving on from our previous articles, I have devised a summary table (table 1) looking at what can or cannot be provided by the existing techniques and what may be provided by the newer techniques that will be discussed briefly in this article. Table 1. Comparative features of plaque imaging tools Future plaque imaging techniques Raman spectroscopy Figure 1. Co-registration of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) images (A) with Raman spectroscopy data (B) Raman spectroscopy is an established analytical technique that is widely utilised throughout the world. Over the last decade, a Raman spectroscopy catheter system has be
July 2010 Br J Cardiol 2010;17:190-3
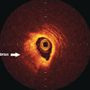
From patient to plaque. Contemporary coronary imaging – part 2: optical coherence tomography
Sudhir Rathore, Scott W Murray, Rodney H Stables, Nick D Palmer

Introduction Table 1. Image characteristics of optical coherence tomography (OCT) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) uses near-infrared electromagnetic radiation, and cross-sectional images are generated by measuring the echo time delay and intensity of light that is reflected or back-scattered from internal structures in the tissue.1,2 Current OCT images are obtained at the peak wavelength in the 1,280–1,350 nm band that enables a 10–15 µm tissue axial resolution, 94 µm lateral resolution at 3 mm, and maximal scan diameter of 6–8 mm (about 10 times resolution as compared with intravascular ultrasound [IVUS]). There are two main tech

