Clinical articles
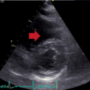
December 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:160 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.037
Troponin biomarkers: the benefits of echocardiography in a presumed diagnosis of NSTEMI
Mark R Jordan, Farhan Shahid, Richard P W Cowell
| Full text
December 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:158 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.036
Risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes among patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation
Debra E Irwin, Michelle Johnson, Simon Hogan, Mark Davies, Chris Arden
| Full text
December 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:128–30 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.031
Hypoglycaemia: patient inconvenience or serious cardiovascular risk?
Vidya Srinivas, Kashif Kazmi, Ketan Dhatariya
| Full text
October 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:153–7 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.033 Online First
Acute coronary syndromes among South Asian subgroups in the UK: symptoms and epidemiology
Simon W Dubrey, Sarah Ghonim, Molly Teoh
| Full text
October 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:159 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.034 Online First
The utilisation of ECG in the Emergency Department
Simiao Liu, Boyang Liu, Han B Xiao
| Full textSeptember 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:113–14 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.027
Provision of cardiopulmonary bypass and surgical backup during TAVI: impact on surgical services
Jon R Spiro, Vinod Venugopal, Peter F Ludman, John N Townend, Sagar N Doshi; on behalf of the UK TAVI Steering Group
| Full text
September 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:117 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.028
Is Alice still in Wonderland of the ‘smoker’s paradox’? A meta-analysis of mortality following ACS
Hisato Takagi, Takuya Umemoto; for the ALICE (All-Literature Investigation of Cardiovascular Evidence) Group
| Full text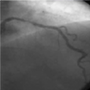
September 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:118–19 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.029
Audit of cardiac catheterisation in a DGH: implications for training and patient safety
Yasir Parviz, Alex Rothman, C Justin Cooke
| Full text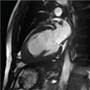
September 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:120 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.030
Endomyocardial fibrosis in hypereosinophilic syndrome
Theodore M Murphy, Deirdre F Waterhouse, Stephanie James, Niamh Murphy, Rory O’Hanlon
| Full text
July 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:108–12 doi :10.5837/bjc.2014.023
Targeting residual risk: a new approach to treating CVD?
Alan Begg, Iain Findlay
| Full text
