
November 2016 Br J Cardiol 2016;23(suppl 2):S1–S12 doi:10.5837/bjc.2016.s02
BJCardio Staff
Abstract

Drug therapies include anticoagulants to reduce the risk of stroke and anti-arrhythmics to restore/maintain the normal heart rhythm or slow the heart rate in patients who remain in AF. Non-pharmacological management options include electrical cardioversion, which may be used to ‘shock’ the heart back to its normal rhythm.
The high risk of stroke associated with electrical cardioversion can be reduced by oral anticoagulation. Although effective in reducing the risk of thromboembolism, the limitations of warfarin present considerable challenges for its use in clinical practice. The challenges of maintaining warfarin within an appropriate th
|
Full text

November 2016 Br J Cardiol 2016;23(suppl 2):S1–S12 doi:10.5837/bjc.2016.s02
BJCardio Staff
Abstract

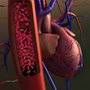
Understanding the mechanisms of AF lies at the heart of its treatment. AF occurs when structural and/or electrophysiological abnormalities alter atrial tissue to promote abnormal impulse formation and/or propagation (figure 1).3 Multiple clinical risk factors, electrocardiographic/echocardiographic features and biochemical markers are associated with an increased risk of AF (table 1), and, AF can be described in terms of the duration of episodes using a simplified scheme (table 2).3
Figure 1. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation
Table 1. Risk factors3
The aim of treatment is to prevent stroke and alleviate symptoms.4 Drug therapies include antic
|
Full text
July 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:(3) Online First
Matthew Rogers
Abstract

We read with interest Diana Gorog’s recent article on the uptake of non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOACS) in the UK.1 She drew attention to the slow uptake of these agents in the UK as opposed to many countries in Europe, and certainly the USA, and to the role that local medicines management committees (MMCs) may play in this. While the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidance regarding all three NOACs available in the UK (apixaban, dabigatran and rivaroxaban) is that they should be available as an option for stroke prevention in non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF), many MMCs in the UK have sought to control p
|
Full text

June 2015 Br J Cardiol 2015;22:61–2
BJCardio Staff
Abstract

Cholesterol lowering significantly reduces stroke in the elderly
Use of cholesterol lowering drugs (statins and fibrates) is associated with a one third lower risk of stroke in older adults without previous disease, finds a study published in the BMJ.
A research team based in France set out to determine the association between use of lipid-lowering drugs in healthy older people and long-term risk of coronary heart disease and stroke. They tracked 7,484 men and women (average age 74 years) with no known history of vascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, living in three French cities (Bordeaux, Dijon and Montpellier).
After an aver
|
Full text
December 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21(suppl 2):S1–S7
Mr Sotiris Antoniou, Dr Chris Arden, Dr Jan Beyer-Westendorf, Dr David Hargroves, Dr Terry McCormack, Professor Gordon McInnes, Dr Raj Patel, Oliver Segal
Abstract

When the NOACs (novel oral anticoagulants) were introduced over three years ago, they promised to revitalise the management of conditions such as atrial fibrillation (AF), venous thromboembolism (VTE) and thromboprophylaxis after major joint replacement surgery. Rivaroxaban is currently available in multiple indications, including (but not limited to): prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular AF, treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults.
For decades anticoagulant therapy in these conditions had relied on the vitamin K antagon
|
Full text

September 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21(suppl 1):S1–S11
Diana A Gorog
Abstract

ESC guidelines and differences between NOACs
Following the roll-out of the novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs), the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) published in 2012 a focused update of its guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation (AF). Since the NOACs tested in clinical trials all showed at least non-inferiority when compared with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs), with a better safety profile, particularly with reduction in intracranial haemorrhage (ICH), the ESC 2012 guideline recommended NOACs as broadly preferable to VKAs in the vast majority of patients with non-valvular AF (NVAF).1 In 2013, the European Heart Rhythm Associati
|
Full text

September 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:105
Dr Andrew Cox
Abstract

New NICE guidance
Dr Andrew Cox (St George’s, University of London)
Stroke prevention is the major focus of the new National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines on atrial fibrillation (AF), which were discussed by Dr Campbell Cowan (Chair, NICE Guidelines Development Group) in one ‘Hot topics’ session at the meeting. This presentation was in anticipation of the release of the final version of the guidelines a fortnight following the conference. This limited discussion covered the already published draft guidance, but points from this draft which were discussed have since been confirmed in the published guidance
|
Full text

September 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:99
BJCardio Staff
Abstract

BSH Parliament day
Professor Andrew Clark (President of the British Society for Heart Failure) is pictured here (centre) carrying out an echocardiogram in the House of Commons. He was at a BSH event to help raise awareness that a person diagnosed with heart failure is likely to have a worse prognosis than if they were diagnosed with most cancers. This is despite the availability of specialist heart failure services that can have a remarkable impact on a patient’s chance of survival, but for which there is inconsistent access over the UK leading to wide variations in care and outcomes. Over 60 MPs, Peers, and professional and patient groups
|
Full text
June 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:58
BJCardio Staff
Abstract

NICE draft guidance on acute heart failure published
The draft acute heart failure clinical guideline from the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is now out for consultation with stakeholders. Guideline recommendations, available on http://www.nice.org.uk, include advice that people with suspected acute heart failure should be seen by a specialist team with a heart failure service at hospital. Currently practice is not standardised across hospitals and many patients are not treated by a dedicated service.
…and also on ICDs and CRT
Draft technology appraisal guidance on the most clinically and cost-effective impla
|
Full text

April 2014 Br J Cardiol 2014;21:69–71 doi:10.5837/bjc.2014.009 Online First
Raza Alikhan
Abstract

Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects up to 2% of the population, its prevalence increasing with age; and, with the anticipated rise in the average age of the population, it is likely that the rate of AF will rise considerably. There is a significant risk of stroke, heart failure and mortality associated with AF. Both the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and National Health Service (NHS) Improvement have identified AF and stroke prevention as key areas for maintaining healthcare quality and improvements.1 A key feature is the early identification of patients at risk of thromboembolic events and the prompt init
|
Full text











