Ethnicity
There is considerable variation in obesity prevalence between different ethnicities in England (see figure 4).6–11
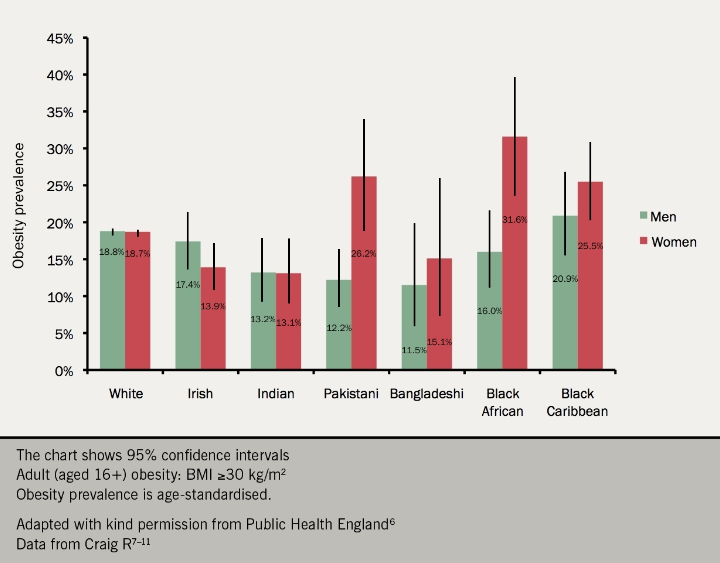
The point at which the level of body fat becomes risky to health varies between ethnic groups, and the validity of using current definitions of obesity for non-white minority ethnic groups is debatable. Different ethnic groups are associated with a range of different body shapes, and different physiological responses to fat storage.12
Evidence suggests that people from black, Asian and other minority ethnic groups are at an equivalent risk of diabetes and other health conditions at a lower BMI than white populations (see later section).
Costs
The cost to society and the economy of people being overweight or obese was estimated at almost £16 billion in 2007 (more than 1% of gross domestic product). Spending on obesity in 2007 accounted for 6% of NHS costs. As obesity levels continue to increase, it is estimated that the combined costs of treating obesity-related diseases increase by £1.9–2 billion per year in the UK.13,14
Recognising comorbidities
Obesity leads to both chronic and severe medical conditions. It is estimated that life expectancy is reduced by an average of two to four years for those with a BMI of 30 to 35 kg/m2, and eight to 10 years for those with a BMI of 40 to 50 kg/m2.15
Doctors of all specialties will increasingly be confronted with patients in whom obesity has modified the presentation and treatment needs of the diseases it causes (see figure 5).1
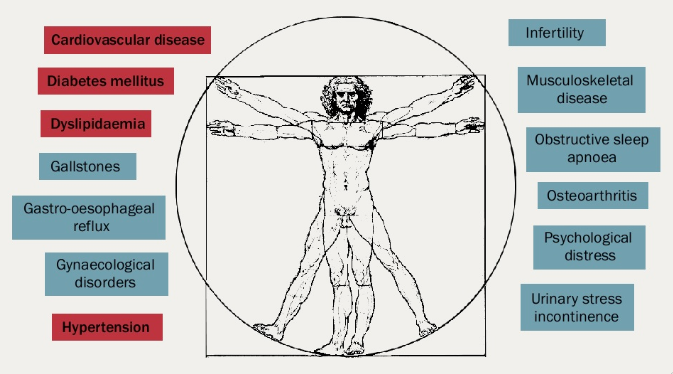
Increasing body fatness is associated with serious medical complications, including:2
• Type 2 diabetes
– 90% of people with type 2 diabetes have a BMI of >23 kg/m2
– obesity is the most potent risk factor for type 2 diabetes and accounts for 80–85% of the overall risk of developing the condition16
• Hypertension
– associated with a five-fold risk in obesity
– 66% of hypertension is linked to excess weight
– 85% of hypertension is associated with a BMI >25 kg/m2
• Dyslipidaemia
– progressively develops as BMI increases from 21 kg/m2 with rise in small particle low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
– people who are obese ( > 30 kg/m2) are more likely to have higher levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, and lower levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol than people who aren’t obese17
• Coronary artery disease (CAD) and stroke
– associated with a 2.0 and 2.4 fold risk in obese men and women, respectively, under the age of 50 years
– 70% of obese women with hypertension have left ventricular hypertrophy
– obesity is a contributing factor to cardiac failure in >10% of patients
– overweight/obesity plus hypertension is associated with increased risk of ischaemic stroke
• Respiratory effects
– a neck circumference of >43 cm in men and >40.5 cm in women is associated with obstructive sleep apnoea, daytime somnolence and development of pulmonary hypertension
• Cancers
– 10% of all cancer deaths among non-smokers are related to obesity (30% of endometrial cancers).
– a recent study has shown that BMI is associated with 17 of 22 cancers. Each 5 kg/m2 increase in BMI was roughly linearly associated with cancers of the uterus, gallbladder, kidney, cervix, thyroid and leukaemia18
• Reproductive function
– 6% of primary infertility in women is attributable to obesity
– impotency and infertility are frequently associated with obesity in men
• Osteoarthritis (OA)
– frequent associated with increasing body weight in the elderly – risk of disability attributable to OA is equal to that of heart disease and greater than any other medical disorder of the elderly
• Liver and gall bladder disease
– excessive weight and obesity is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). 40% of NASH patients are obese; 20% have dyslipidaemia
– three-fold risk of gall bladder disease in women with a BMI of >32 kg/m2; 7 x risk if BMI of >45 kg/m2
More recently, associations have been recognised between obesity and several cancers, Alzheimer’s disease and renal failure.19
